Population health management (PHM) was a central theme again at HIMSS this year, with an expansive set of companies linking themselves to the phrase in one fashion or another. In fact, almost 125 companies were listed as PHM exhibitors in the HIMSS program. Given the broad definition of population health management, the number of banners, pamphlets, and swag showcasing the phrase on the conference floor was not surprising.
Last year, we wrote about payers’ shift beyond traditional fee-for-service to alternative payment models, which continues to drive the buzz around and demand for PHM offerings. PHM capabilities are utilized across the continuum of care and companies from diverse backgrounds, including payers, providers, and service and technology vendors, are leveraging their competencies to enable the shift to value-based care, all under the banner of “population health management.”
The implications of the hype around PHM are twofold: (1) organizations in the market for PHM solutions are faced with the daunting task of distinguishing between vendors, understanding what capabilities are provided, and what solutions are viable and (2) vendors must find unique ways to differentiate themselves from every other vendor branded as a PHM company.
While some companies provide a more comprehensive solution, most specialize in one area that solves for a specific need within a value-based care model. TripleTree established a framework of four major categories of solution vendors to use as a means of reducing the noise in the marketplace and distinguishing between the overwhelming number of PHM vendors. The diagram below is a visual depiction of TripleTree’s framework with brief insights into the four major categories.
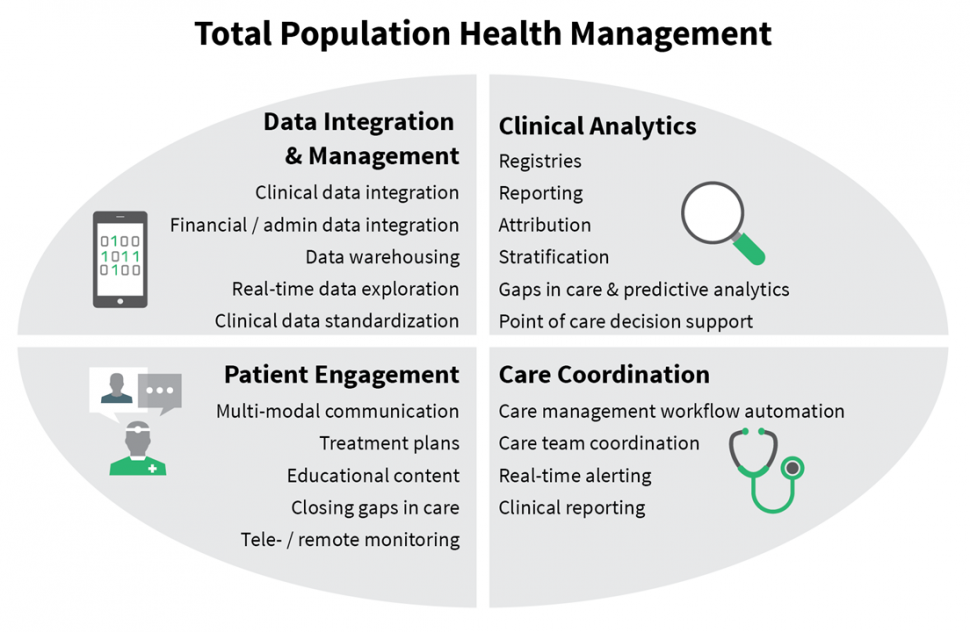
Data Integration and Management
A few examples of solutions and capabilities in this space include enterprise data warehousing (EDW), clinical data standardization, and data integration. Aggregating, integrating, and managing clinical data are key tools and a necessity with any PHM strategy.
At HIMSS this year, Health Catalyst announced a new product roadmap that will in part, expand on its core EDW offering and strengthen other PHM capabilities. A few examples from the company’s roadmap include incorporating a natural language processing component to the core platform, integrating clinical data with genomic data, and integrating de-identified data from 65 million patient records into a single repository.
Numerous companies with data integration and management capabilities have been acquired over the past few years, including Humedica (acquired by Optum in 2013), dbMotion (acquired by Allscripts in 2013), and Explorys (acquired by IBM in 2015). Alongside Health Catalyst, Lumeris and Sandlot Solutions are other independent vendors with capabilities in this segment.
Clinical Analytics
Data integration and management enable a variety of capabilities that support PHM strategies, including risk stratification, gaps in care and predictive analytics, clinical decision support, etc. Just prior to HIMSS, IBM became an even larger player in this segment when it announced its plans to acquire Truven Health Analytics. The acquisition will significantly increase the data management and analytics capabilities of IBM’s Watson Health while adding 8,500+ customers to the platform.
Forward Health Group and Jvion are two other representative vendors finding success in this segment by bringing differentiated approaches to market.
Care Coordination
Care coordination was a key theme of its own at HIMSS this year – albeit often under the guise of PHM – with solutions that empower providers and care teams to efficiently coordinate the services provided to patients across the continuum of care in an effort to manage cost and quality. CareSync, who raised capital about six months ago, Curaspan, and Fitango are a few of the vendors at HIMSS marketing their capabilities in this segment.
Last fall, we wrote a blog examining the care coordination landscape and relationships amongst market constituents and we continue to see traction in this segment as the market shifts to value-based care models.
Patient Engagement
Examples of solutions falling within patient engagement include those that provide multi-modal communication capabilities, treatment plans and education content, and tele- / remote monitoring capabilities, among others. Engaging patients and providing a means for them to interact directly with providers helps solve for non-adherence issues and close gaps in care.
Vivify Health has gained momentum by offering an intuitive remote care management platform and recently received a strategic investment from UPMC, which joined a number of other strategic investors. UPMC has invested in several other PHM providers, including Health Catalyst and MedCPU, and will serve as both a customer and development partner to each organization.
In addition to the companies referenced above, we are following a number of others in the space and are eager to watch and learn about how companies differentiate themselves in the market. Further, we believe investment and M&A activity across the population health management landscape will remain high in 2016 and we will be actively monitoring the sector. If you were at HIMSS this year and would like to discuss population health management or other themes from the conference, let us know.